
03 Respiratory System 3ESOBiologyGeology
Anaerobic respiration in animals. Anaerobic respiration mainly takes place in muscle cells during vigorous exercise. When we exercise at high intensities, our muscles have a higher demand for energy. Our bodies can only deliver so much oxygen to our muscle cells for aerobic respiration. When oxygen runs out, glucose is broken down without it.
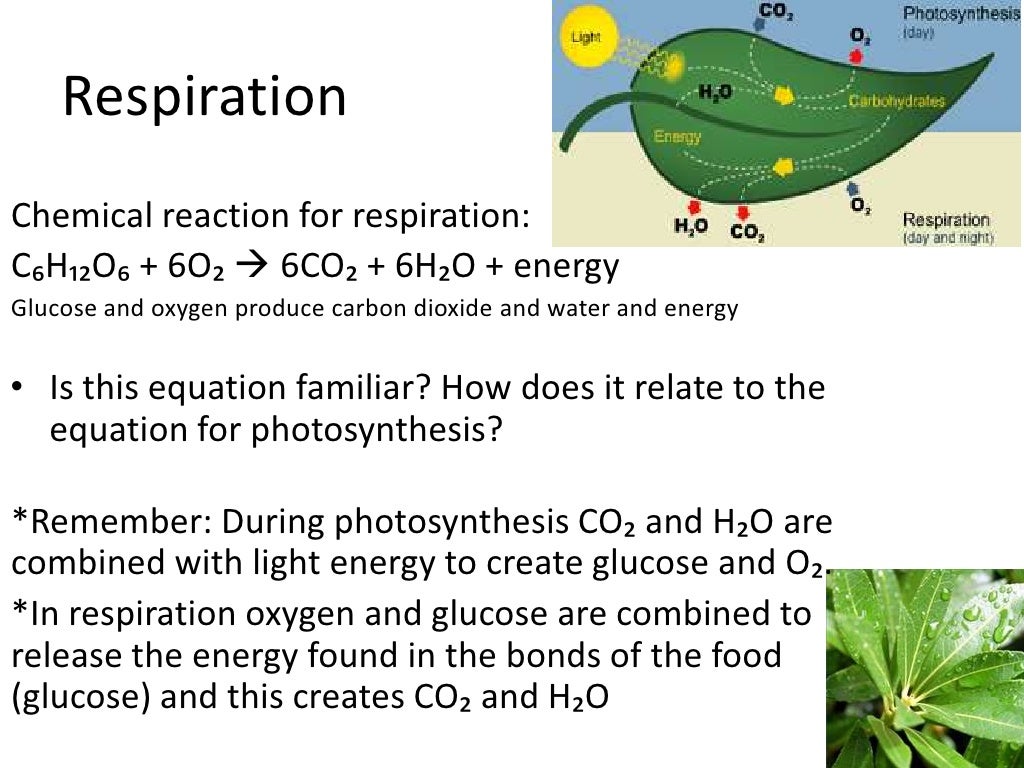
Plant processes respiration
Anaerobic respiration allows plants and fungi to produce energy even when there is a lack of oxygen, allowing them to survive and grow in conditions where oxygen is limited. This is important for the survival of both plants and fungi in environments with low oxygen levels. →How is fermentation related to anaerobic respiration in plants and.
Balanced Chemical Equation For Anaerobic Respiration In Muscles Tessshebaylo
Lára has a particular interest in the area of infectious disease and epidemiology, and enjoys creating original educational materials that develop confidence and facilitate learning. Revision notes on 5.2.8 Anaerobic Respiration for the AQA A Level Biology syllabus, written by the Biology experts at Save My Exams.

Give The Balanced Chemical Equation For Cellular Respiration Tessshebaylo
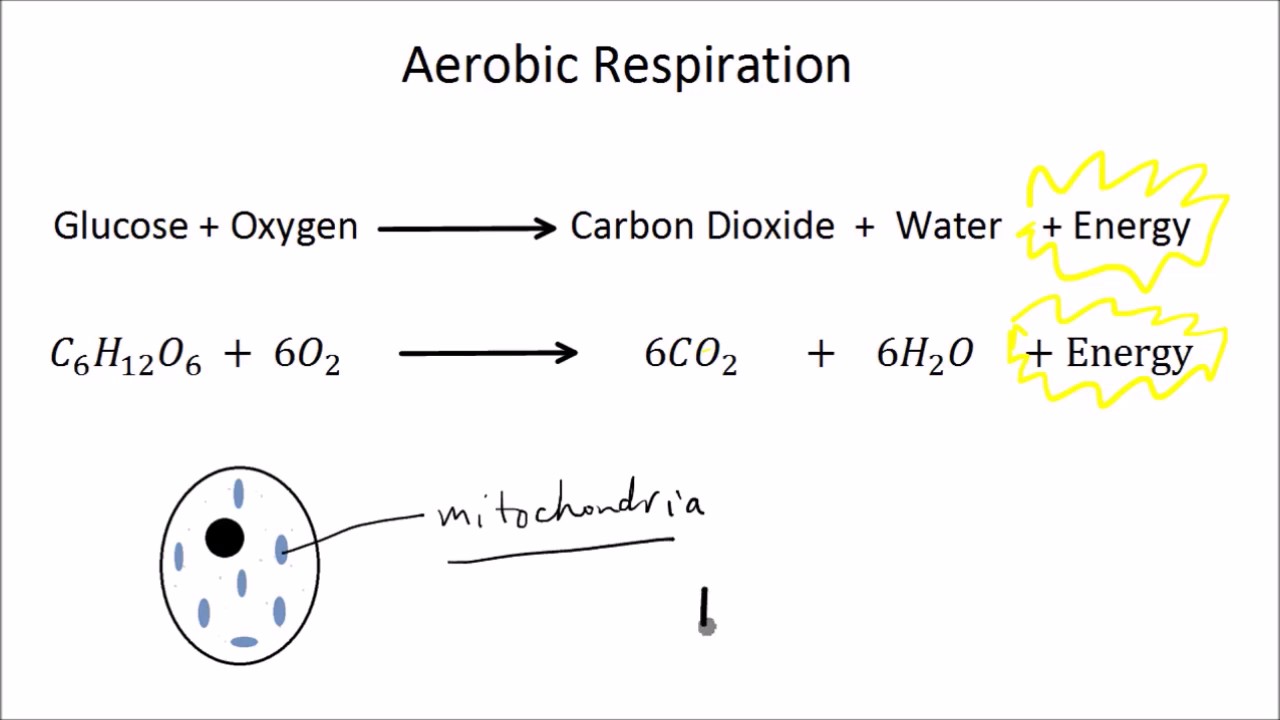
The chemical reaction is given below: C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 -> 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O + energy (as ATP) Anaerobic Respiration :It occurs in the cell cytoplasm in the absence of oxygen. Anaerobic respiration involves partial oxidization of glucose forming ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide as end products. It involves glycolysis.
Respiration OCR — the science sauce
Anaerobic respiration is a critical component of the global nitrogen, iron, sulfur, and carbon cycles through the reduction of the oxyanions of nitrogen, sulfur, and carbon to more-reduced compounds. The biogeochemical cycling of these compounds, which depends upon anaerobic respiration, significantly impacts the carbon cycle and global warming.
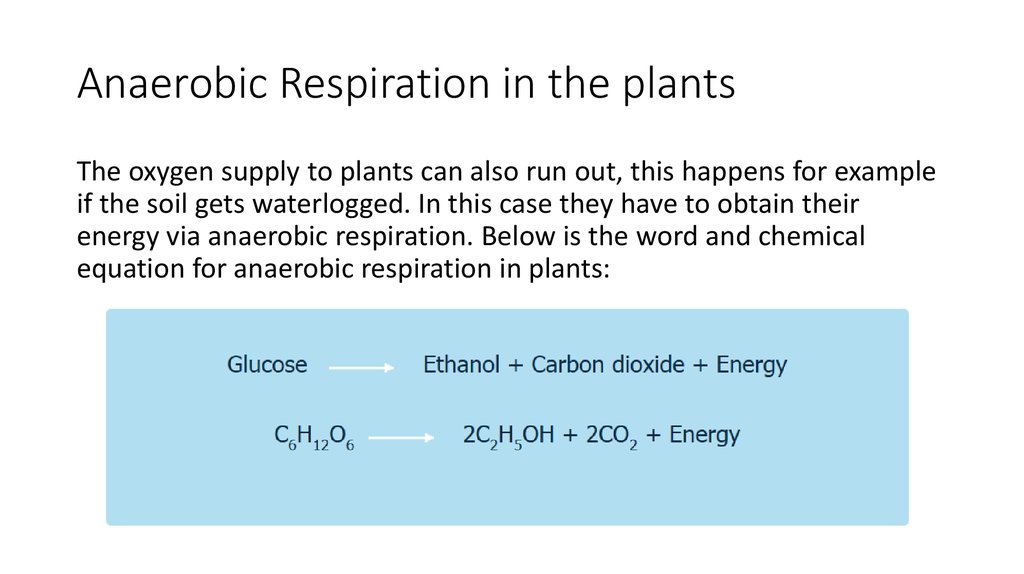
Balanced Chemical Equation For Anaerobic Respiration In Plants My XXX Hot Girl
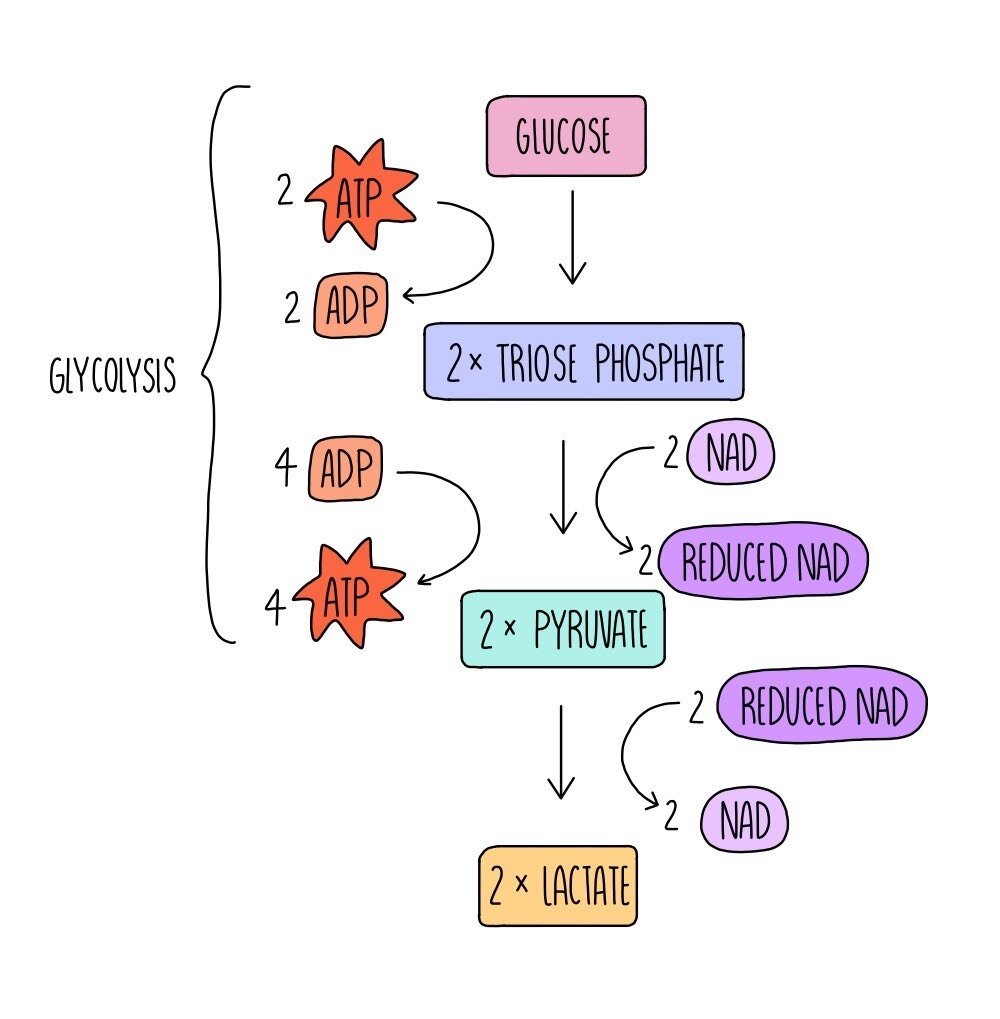
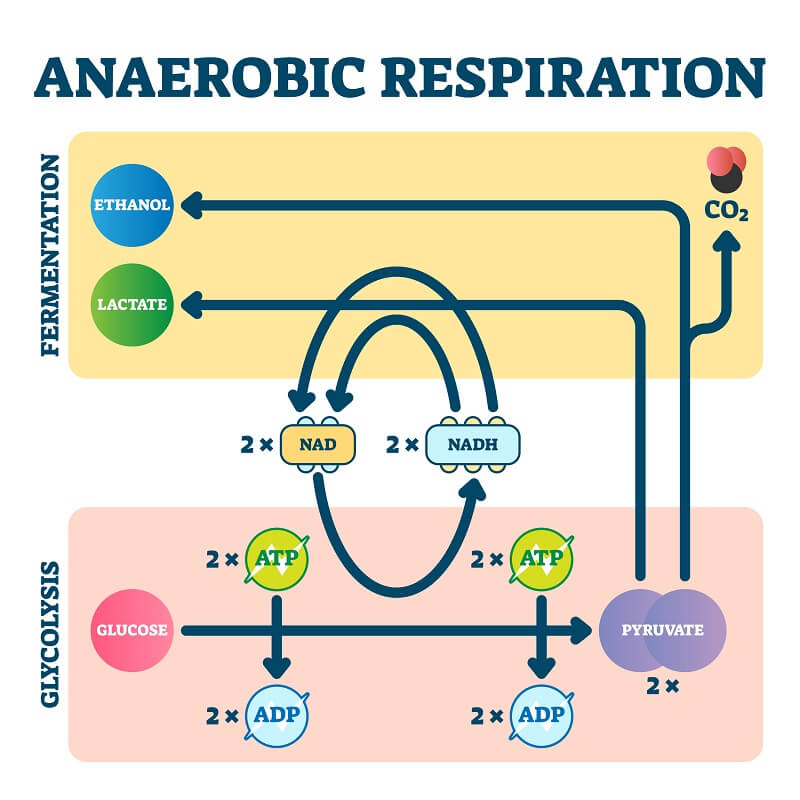
Anaerobic Respiration Equations. The equations for the two most common types of anaerobic respiration are: • Lactic acid fermentation: C 6 H 12 O 6 (glucose). Unfortunately, alcoholic fermentation isn't the only kind of fermentation that can happen in plant matter. A different alcohol, called methanol, can be produced from the.
Aerobic Respiration
Q.5. How does anaerobic respiration differ in plants and animals? Ans. The differences in anaerobic respiration between plants and animals are: a. In plants, the end products are ethanol and CO 2. In animals, the end product is lactic acid. b. In plants, the accumulation of ethanol may kill the plant. In animals, the lactic acid cannot cause.
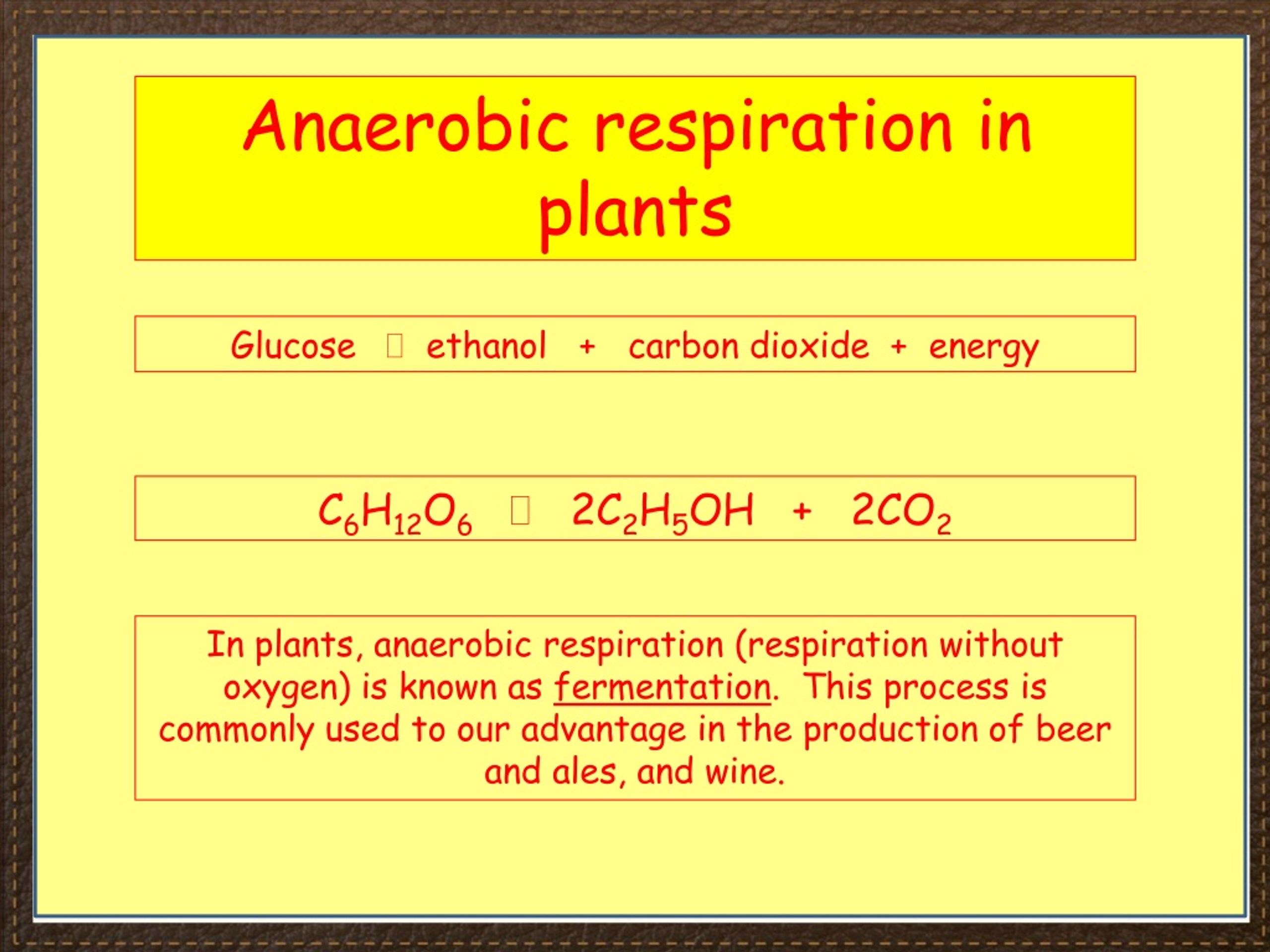
PPT iGCSE Biology Section 2 lesson 4 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID8926275
Fermentation is another anaerobic (non-oxygen-requiring) pathway for breaking down glucose, one that's performed by many types of organisms and cells. In fermentation, the only energy extraction pathway is glycolysis, with one or two extra reactions tacked on at the end. Fermentation and cellular respiration begin the same way, with glycolysis.
Breathtaking Word Equation For Anaerobic Respiration In Plants Physics Aqa A Level Data Sheet
The word equation for aerobic respiration is:. These organisms and tissues use the process of anaerobic respiration close anaerobic. Yeast: ethanol and carbon dioxide. Some plants: ethanol.

vegetarian diagramă baie anaerobic respiration in plants INSCRIETI Sediu Ce drăguț
Anaerobic respiration in plants Certain plants, and plant cells also respire anaerobically. These include plants that grow in marshes, where oxygen concentrations will be low.

Aerobic Respiration 88Guru
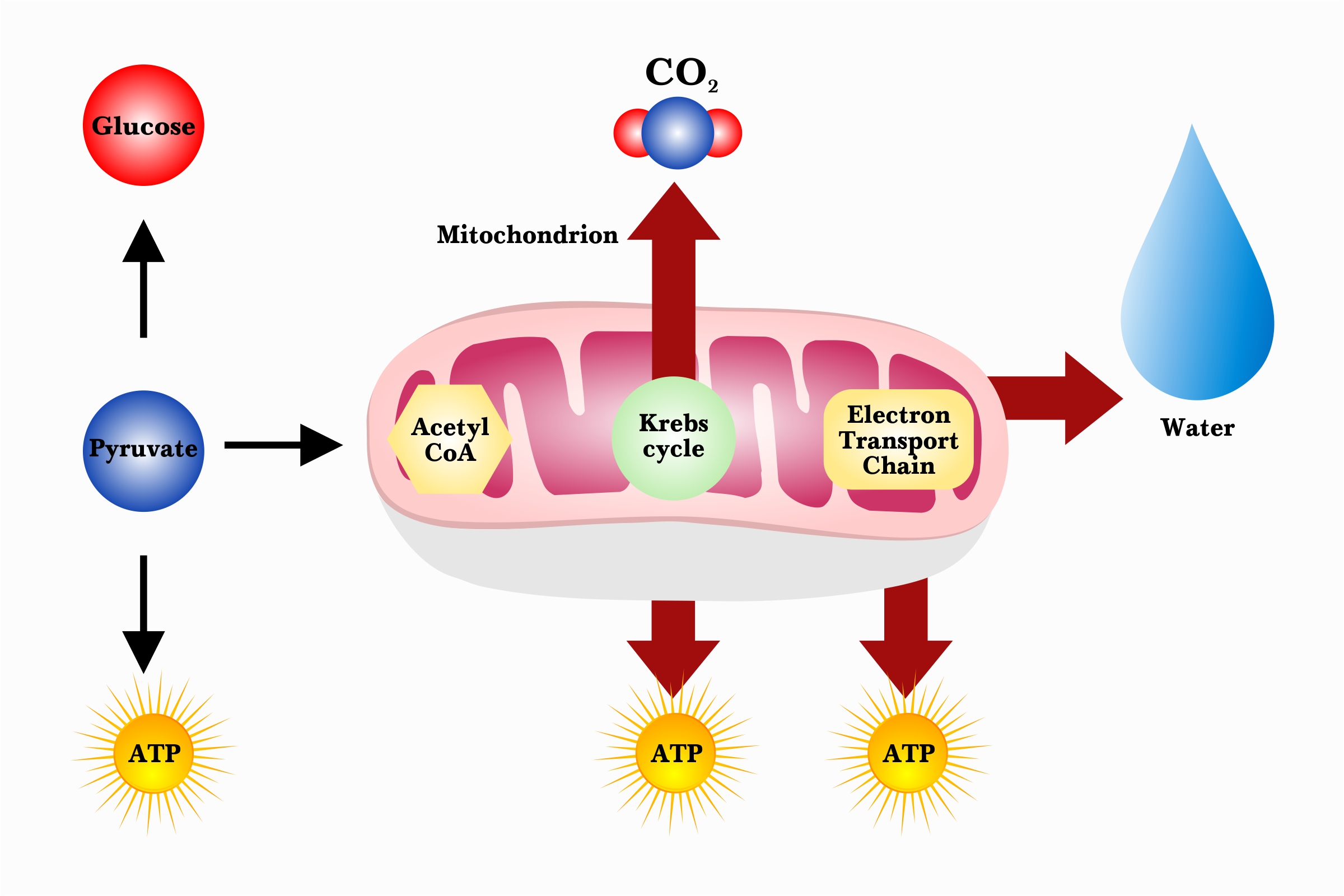
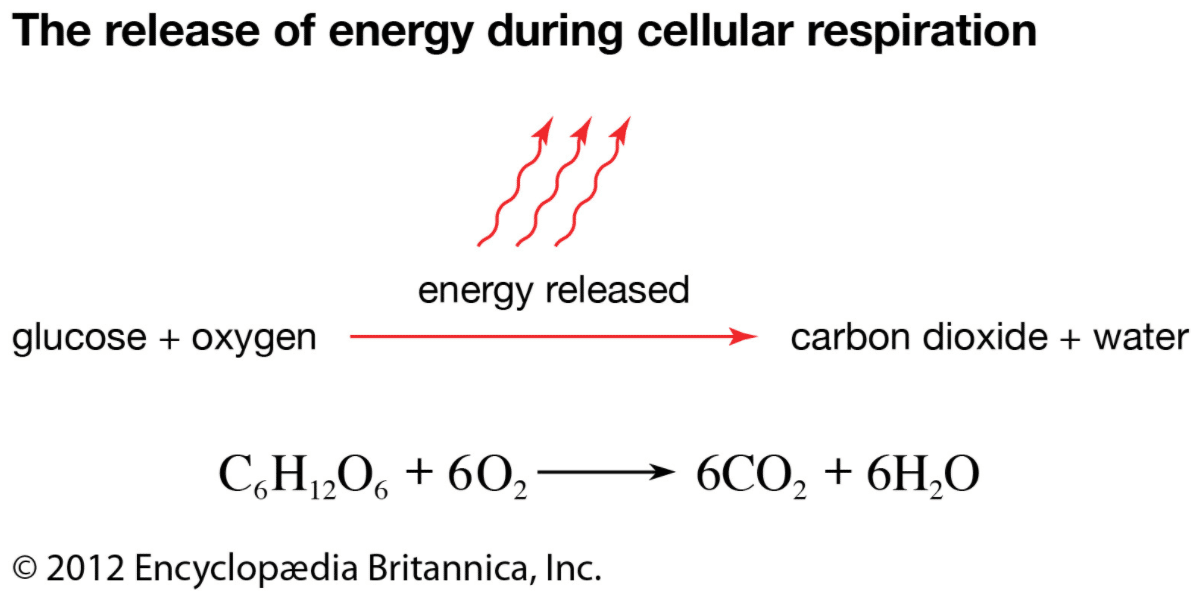
Cellular respiration. Cellular respiration is a biochemical process of breaking down food, usually glucose, into simpler substances. The energy released in this process is tapped by the cell to drive various energy-requiring processes. Cellular respiration can occur both aerobically (using oxygen), or anaerobically (without oxygen).

Respiration (A Level) — the science hive
Advantages of Anaerobic Respiration. One advantage of anaerobic respiration is obvious. It lets organisms live in places where there is little or no oxygen. Such places include deep water, soil, and the digestive tracts of animals such as humans (see Figure below). E. coli bacteria are anaerobic bacteria that live in the human digestive tract.
45 best ideas for coloring Cellular Respiration Equation
The primary difference between aerobic and anaerobic respiration is the presence or absence of oxygen during the processes. More detailed differences between the two are as follows: Aerobic Respiration. Anaerobic Respiration. Oxygen is present when this form of respiration takes place. Oxygen is absent when this form of respiration takes place.

Cellular Respiration Takes in food and uses it to create ATP, a chemical which the cell uses
Figure 7.14.1 7.14. 1: Anaerobic bacteria: The green color seen in these coastal waters is from an eruption of hydrogen sulfide-producing bacteria. These anaerobic, sulfate-reducing bacteria release hydrogen sulfide gas as they decompose algae in the water. Eukaryotes can also undergo anaerobic respiration.
Cellular Respiration In Plants Definition Steps Equat vrogue.co
Aerobic respiration occurs in most of the higher species including plants and animals. Cellular respiration in humans is an example. In anaerobic respiration, the process occurs in the absence of oxygen. Examples of an anaerobic respiration equation are the following: Denitrification: NO3− → NO2−→ NO + N2O → N2.

Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration Equation • Suggested and Clear Explanation of Quizlet
The term anaerobic respiration is often used in connection with higher organisms where it occurs in the roots of some water-logged plants, muscles of animals and as supplementary mode of respiration in massive tissues. Anaerobic respiration is the exclusive mode of respiration in some parasitic worms, many prokaryotes, several unicellular.
- Donde Puedo Ver Gigante De Acero
- Curso Formacion Basica Maritima Galicia
- Canelones De Atun Huevo Y Tomate
- Corrector Ortografico Desde Este Altozano Se Dibisan Plantaziones De Cerezos
- Rompecabezas De Madera 3d De Natura Bola
- After En Mil Pedazos Hd Castellano
- Doe Eyes Love Theme From The Bridges Of Madison County
- Asociaciones De Mayores En Vitoria
- Rige En La Sucesión Intestada La Transmisión Del Ius Delationis
- Ejercicios Con Banda Elastica Para Futbolistas